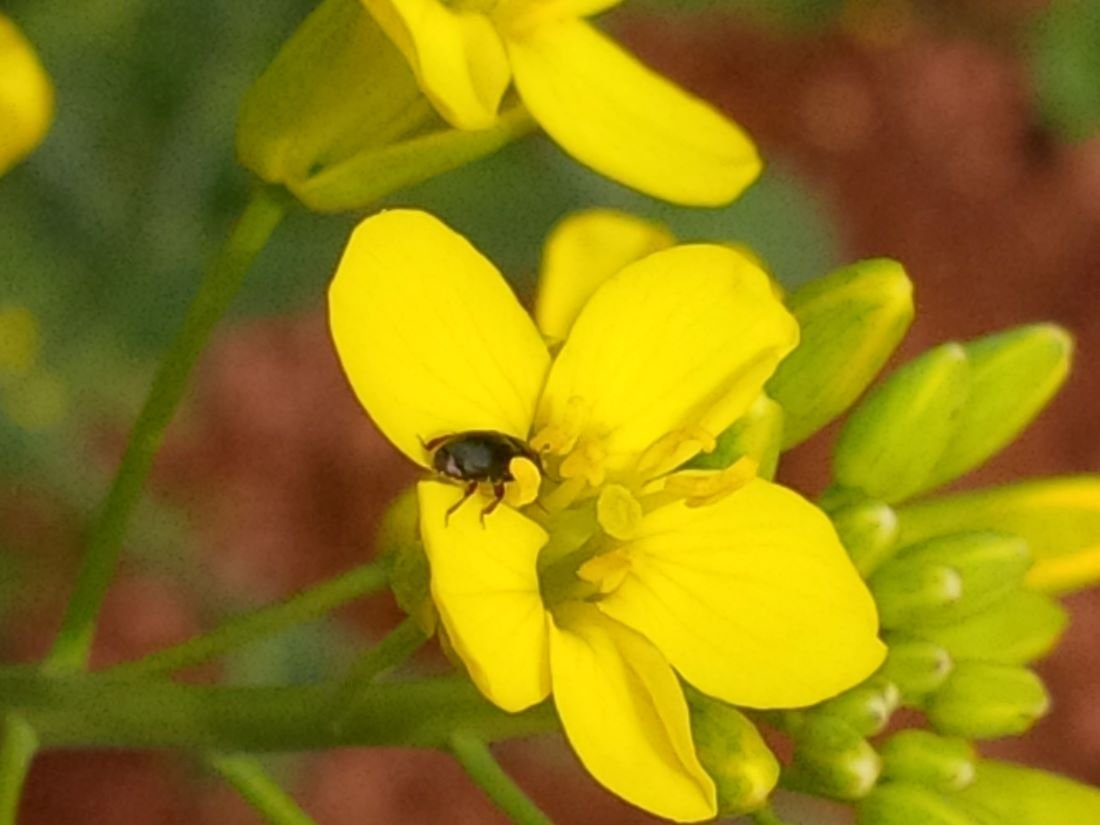
Generate knowledge and control strategies for the pollen beetle Brassicogethes viridescens (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae), a new invasive insect pest of canola
Date: March 31, 2022
Term: 4 years
Status: Complete
Researcher(s): Christine Noronha, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada
SaskCanola Investment: $61,800
Total Project Cost: $185,400
Funding Partners: Alberta Canola, Manitoba Canola Growers Association
Key Result
Pollen beetles were susceptible to three of four insecticides tested. Yield reduction was detected at 7-9 beetles per plant but not at four beetles per ten sweeps. Pollen beetles were not detected in the Prairie provinces and no native parasitoids were found attacking pollen beetle larvae in Atlantic Canada.
Project Summary
The pollen beetles is an invasive pest of canola. Originally from Europe, it is found in Atlantic Canada and Quebec. Climate models show a high potential for it migrating to western Canada where canola is a major crop. The lack of basic information about this invasive pest prompted this research project. The main objectives were to determine an economic threshold and evaluate the efficacy of insecticides less toxic to bees since this pest is found feeding and laying eggs when the crop is in bloom. The canola crop in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba was monitored for presence of this pest.
Cages in a canola field
Methodology
To determine the economic threshold the trials was conducted within field cages to eliminate the influence of other insects pests on yield, wild bees were placed in the cage for pollination. Plant samples were also collected from outside the cages to compare the influence of other pests on yield. Noronha’s research team also conducted sweep net sampling, a common method used for sampling canola to determine population levels in 2021 and related it to damage.
Heavy rain and wind in July and August could have influenced the yield and beetle population outside the cages. Sweeping the field during flowering can also remove flowers which can result in pod loss. The data from inside the cages would be more reliable. Cages can impact oil and protein content.
Canola plants in field cage
Results
This project has provide a better understanding of the economic impact of the pollen beetles alone if populations were allowed to increase. The research team found that a threshold 7-9 beetles per plant can cause significant yield loss in the absence of other pests. Sweep net sampling in 2021 showed that in the presence of other pests an average of 4 beetles per sweep gave 18% pod loss. This project also showed that the insecticides that have a reduced risk to bees, were efficacious at the low rate making two or more application that are generally required to control immigrating pollen beetles during the flowering stage a more feasible option. This research has shown that pollen beetle has not yet been found in ON, MB, SK, and AB, however monitoring should continue. The lack of native parasitoids indicates that evaluation of biocontrol agents from Europe should be considered.
Conclusions
This project discovered that pollen beetles have only one generation per year with an obligatory diapause. The research team found that populations in Canada can be controlled by the low rate of insecticides that have a reduce impact on bees. This knowledge together with the thresholds established in this study will aid in decisions to time applications of insecticides for optimum control within an IPM program. Pollen beetles not yet found in Western Canada but surveys should continue.
Recommendations
In the future, farmers should have a choice of different insecticides to rotate for pollen beetle control (once registered in Canada). Establishing a threshold of 7-9 pollen beetles per plant will assist in decisions on the timing of insecticide application. Although pollen beetles were not discovered in the Prairie provinces, continued vigilance is recommended.
Damage caused by pollen beetle
Pollen beetle feeding
Adults plus damage
Photo credit for all photos: Noronha’s research team.